#

Drupal
Build simple or complex websites and apps with a leading open source CMS.
Drupal is one of the world's most popular open source content management systems! Build simple or complex websites and apps and get access to a rich ecosystem of tools and themes.
#
Prerequisites
- Have an existing AWS Account.
- Have an existing EC2 Pair Key
- Preexisting VPC LAUNCH STACK
#
CMS Subscription
The following steps cover the setup of the Drupal Pro on the AWS Marketplace. Click the “Continue to Subscribe” button at the top of the AWS Marketplace listing page to continue the process. Drupal Pro is available as a monthly subscription on the AWS Marketplace. The subscription includes the software's operational and infrastructure costs for running on AWS.
- Subscribe to Solodev on the AWS Marketplace. SUBSCRIBE
- Review and accept the "Terms and Conditions".
- Click "Continue to Configuration".

NOTE:
Once accepted, you will receive a thank you message asking you to configure your software.
This process can take a few moments. Please do not exit the screen or refresh the page.
#
Configure Software
- Choose a fulfillment option and software version to launch this software.

- Click "Continue to Launch."

Important:
On the next screen, click on "Usage Instructions" and then select the Quickstart link to continue the installation.
#
Launch Software
Review the launch configuration details and follow the instructions to launch this software.
To continue the installation, click the Launch button below and follow the outlined steps.
NOTE:
If your AWS region is different from us-east-1, make sure to select your specific region from the top menu.
#
Create Stack
- Create a stack.
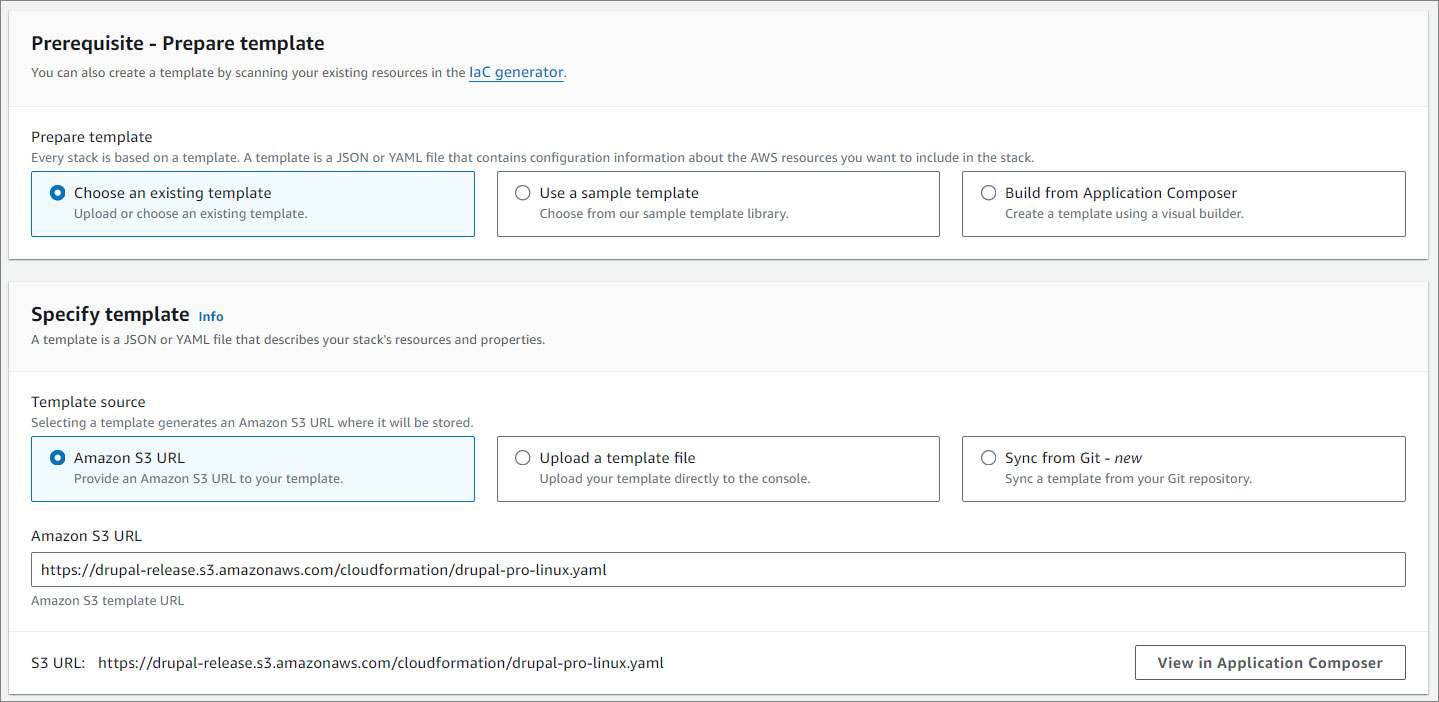
- Click Next.
#
Stack Details
#
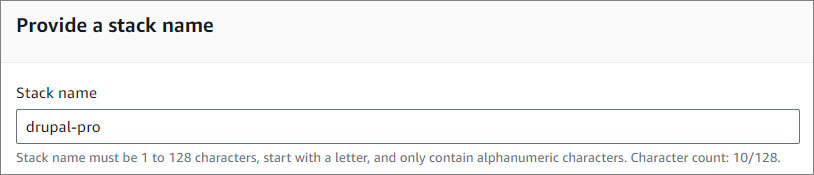
Provide a stack name
- Provide a stack name. Stack name must be 1 to 128 characters, start with a letter, and only contain alphanumeric characters.
#
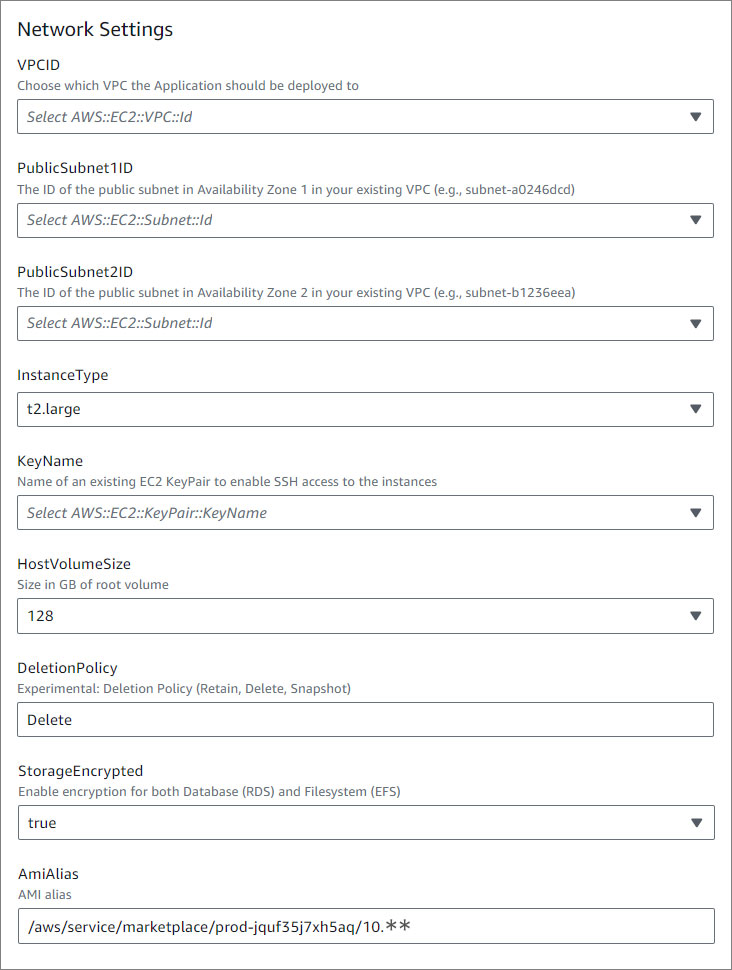
Parameters
- Specify the parameters in the setup section.
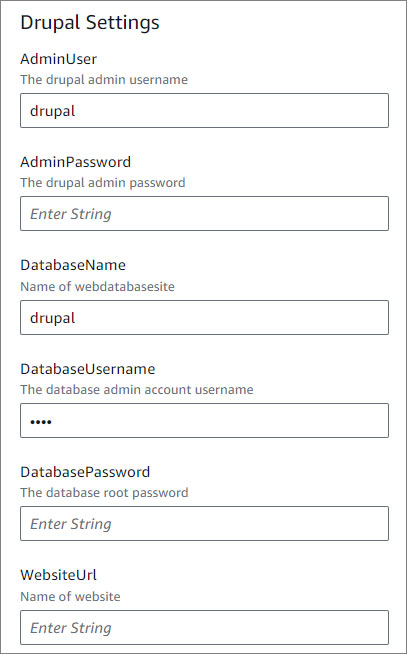
- Drupal Settings.
- Click Next.
#
Configure Stack Options
- Add a new tag. This step is optional.
Tags (key-value pairs) are used to apply metadata to AWS resources, which can help in organizing, identifying, and categorizing those resources. You can add up to 50 unique tags for each stack. If you need more information about tags, click here.
- Specify an existing AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) service role that CloudFormation can assume. This step is optional.
- Select the stack failure options.
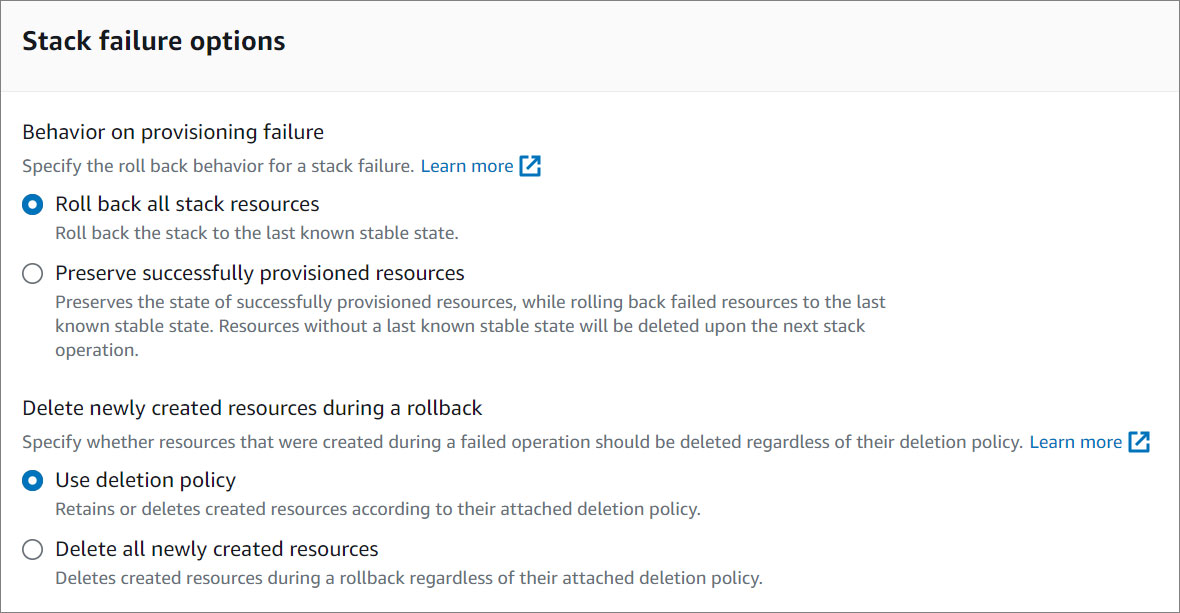
To learn more about the stack failure options, click here .
#
Advanced options
- You can set additional options for your stack, like notification options and a stack policy. For more information, click here .
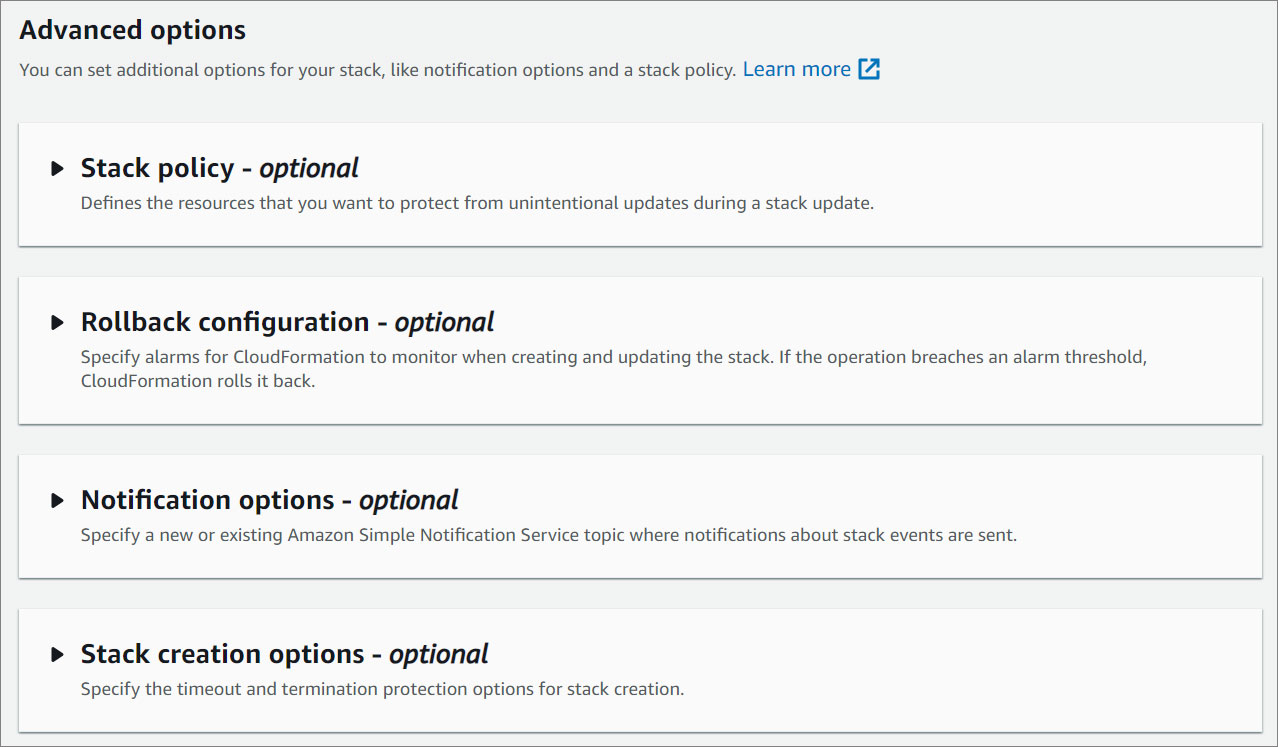
- Click Next.
#
Review and create
Review your settings.
Acknowledge the AWS CloudFormation terms.
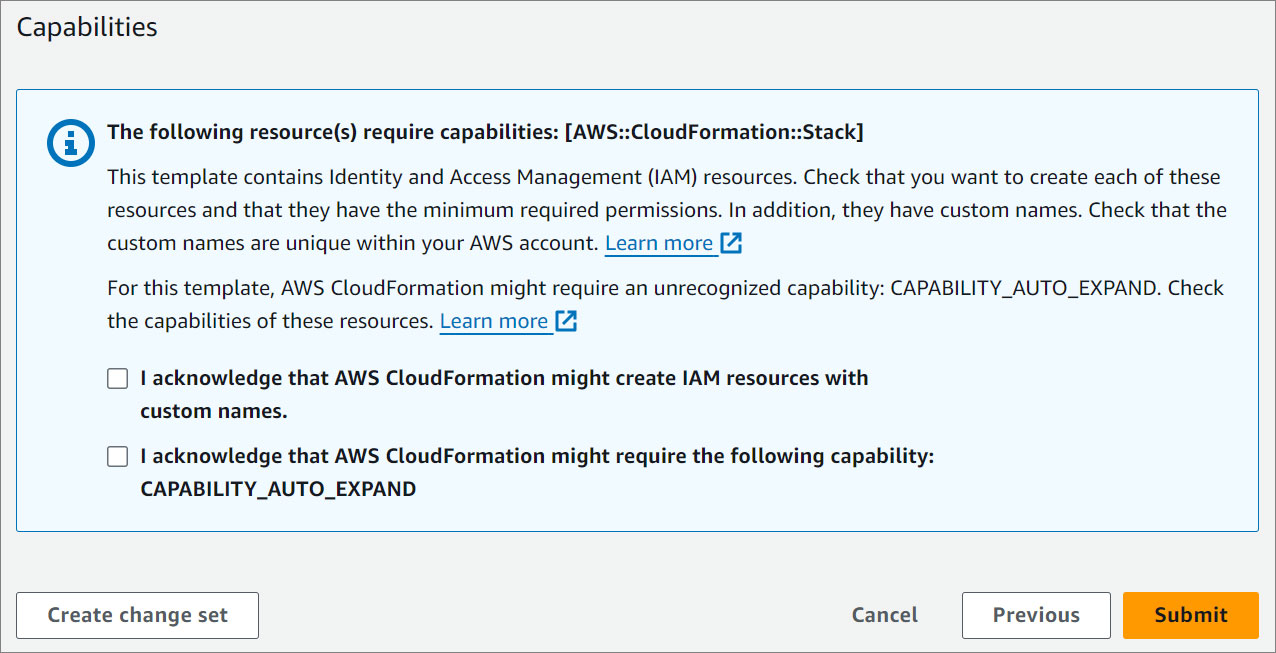
- Click Submit.
#
Stacks
- Watch your CMS being created! Once the status changes from CREATE_IN_PROGRESS to CREATE_COMPLETE, you can access your CMS.
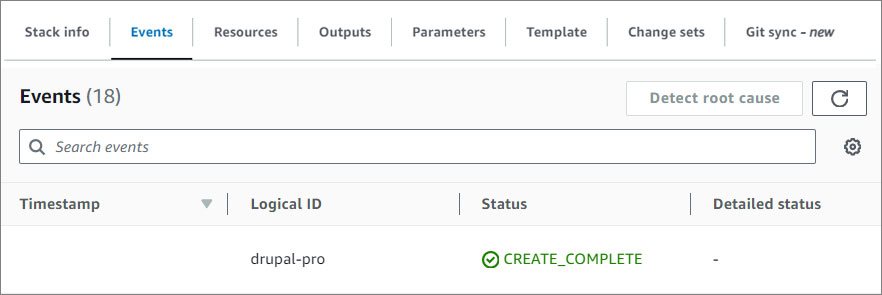
- Click on the Outputs tab and copy the AdminUrl value.
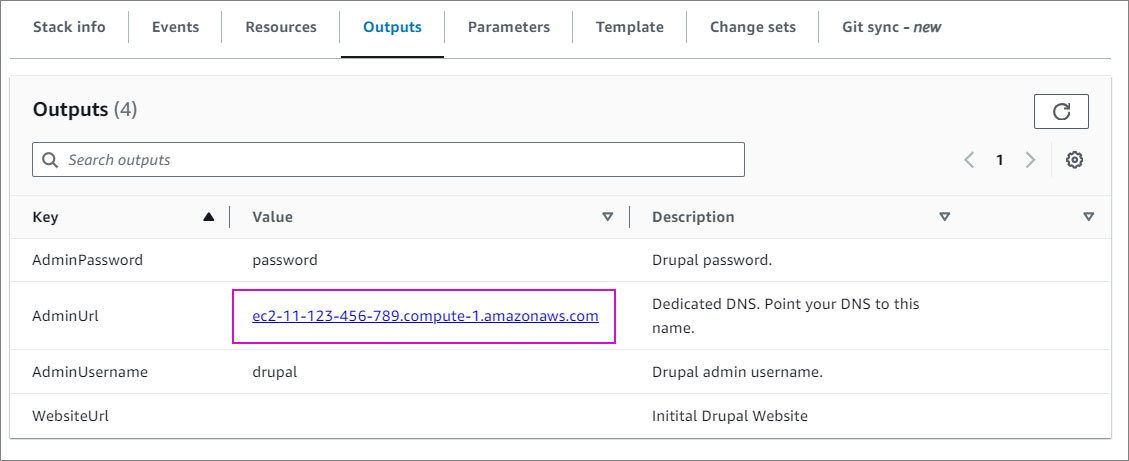
- Open your preferred browser and paste the AdminUrl value to access the Drupal front-end website.
Note:
Ensure that your browser's address bar includes "http://" instead of "https://."
- To access the Drupal login page, add
/user/loginto the end of the website URL. Use the Admin Username and Admin Password provided in the stacks output to log in.
#
Choose an Action
- Select Launch through EC2.
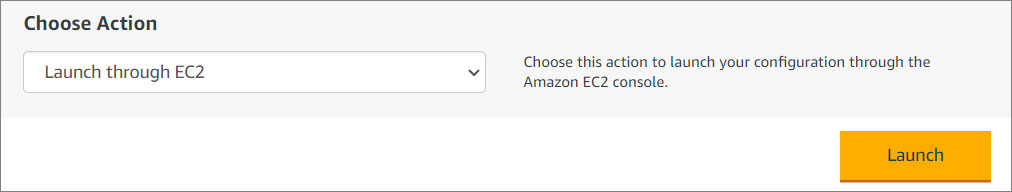
- Click Launch.
#
Launch an instance
Create virtual machines, or instances, that run on the AWS Cloud. Quickly get started by following the simple steps below.
- Name and tags. Give your instance a name. You can also add additional tags (Optional).
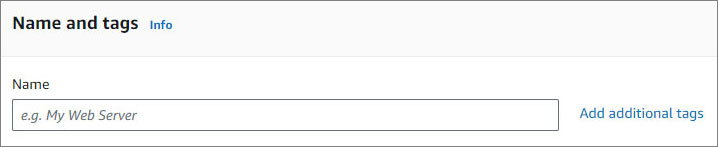
NOTE:
A tag is a label that you assign to an AWS resource. Each tag consists of a key and an optional value, both of which you define.
- Application and OS Images (Amazon Machine Image). An AMI contains the software configuration (operating system (OS), application server, and applications) required to launch your instance.
For more information about Amazon Machine Image, click here .
- Instance Type. Select an instance type that meets your computing, memory, networking, or storage needs.
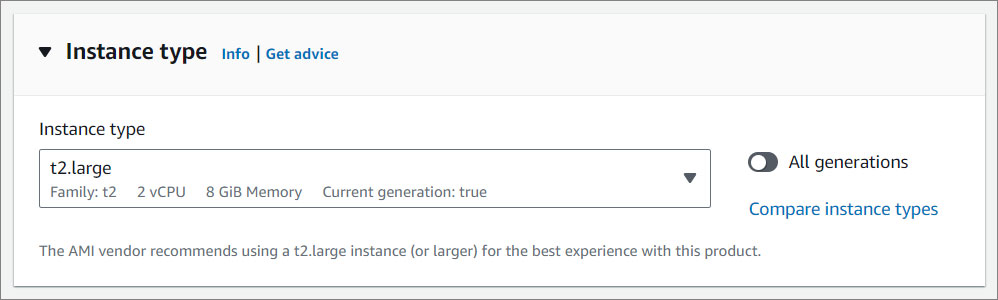
To learn more about which instance to select based on your traffic needs, click here .
NOTE:
Solodev recommends t2.large server. Depending on your traffic needs, you can select an instance size from the available options in the menu.
- Key Pair. You can use a key pair to securely connect to your instance. Ensure that you have access to the selected key pair before you launch the instance.
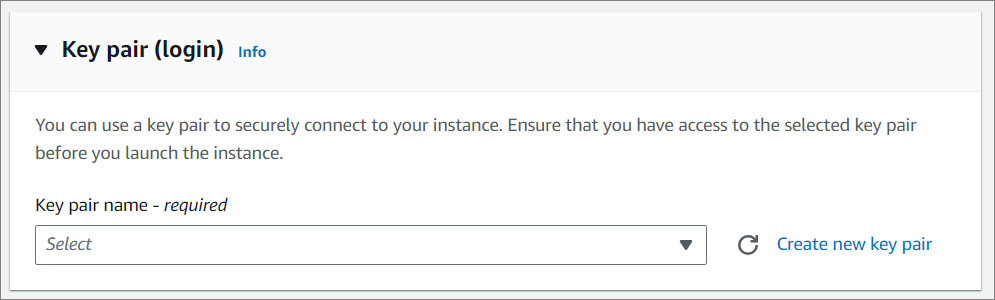
NOTE:
An Amazon EC2 key pair is a set of security credentials consisting of a public and private key that verifies a user's identity when connecting or communicating with an EC2 instance. If you do not have a Key Pair, you will need to create one in your Key Pair Console. For instructions click here .
- Network Settings. Here you can create or select an existing security group, create an instance that can connect using SSH, and more.
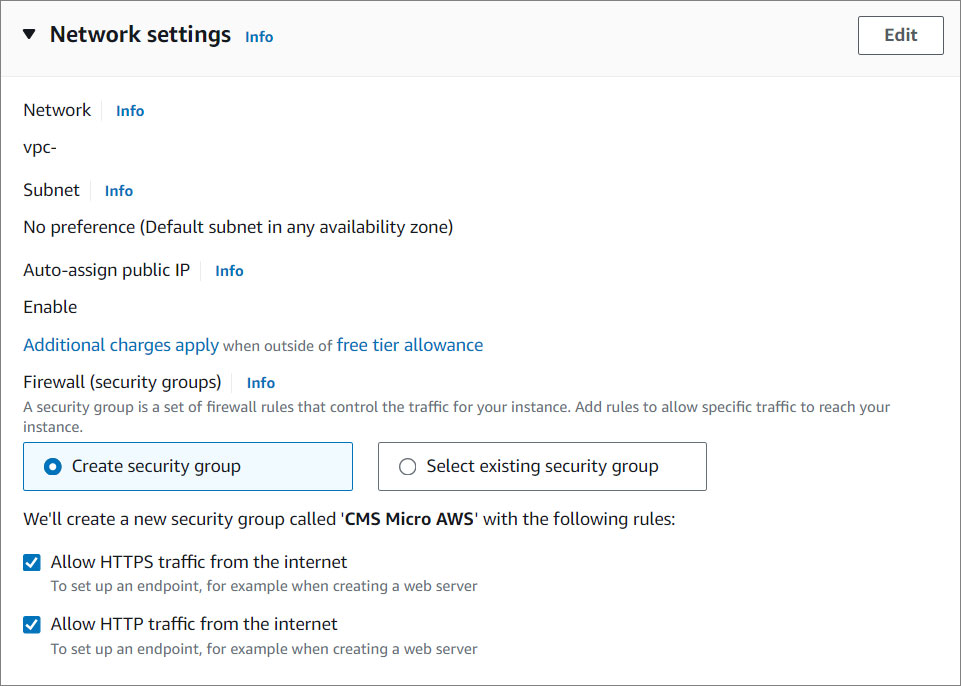
- Configure storage. Specify the storage options for the instance.
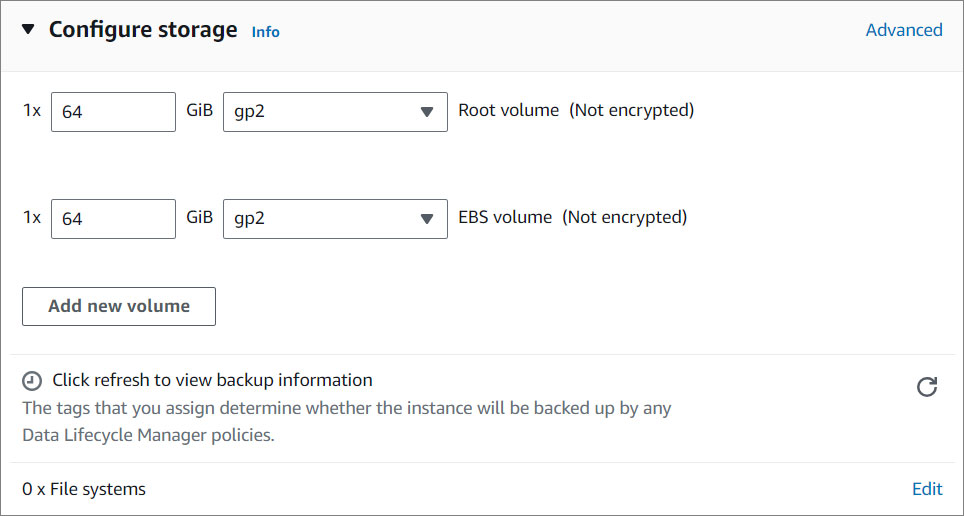
For more information about storage, click here .
Click Launch Instance.
You will get a success message. Click on the ID to access your EC2 Instance.

#
EC2 Instance
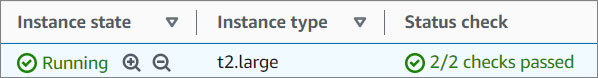
- Check the Instance State and Status Check of your instance. Once your instance state changed from Pending to Running, click on the instance you created to access it.
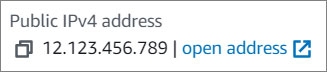
- Click on your Public IPv4 address to access your website.
- To access the Drupal login page, add
/adminto the end of the website URL. Use drupal as the username and your instance ID as the password.
Note:
Ensure that your browser's address bar includes "http://" instead of "https://."
#
Choose an Action
- Select Launch from Website
- EC2 Instance Type. Drupal runs on a single Amazon Elastic Compute (EC2) instance and is defaulted to run on a recommended t2.large server. Depending on your traffic needs, you can select an instance size from the available options in the menu.
To learn more about which instance to choose based on your traffic needs, click here .
- VPC Settings. An Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a dedicated environment that lets you launch the AWS resources that power your Drupal in an isolated virtual network. If you do not have a VPC, you will need to create one in your VPC Console.
For instructions on how to create a VPC, click here for instructions .
- Subnet Settings. A subnet is a range of IP addresses contained in your VPC. You can create AWS resources, such as EC2 instances, in specific subnets, enabling you to group network resources more efficiently.
If you do not have any existing subnets, you will need to create one in your Subnet Console. For instructions, click here .
- Security Group Settings. A security group acts as a firewall that controls the traffic allowed to reach one or more instances. You can create a new security group or choose one of your existing groups. Select an existing security group from the menu or configure a new security group using the form provided. Name your security group and give it a description.
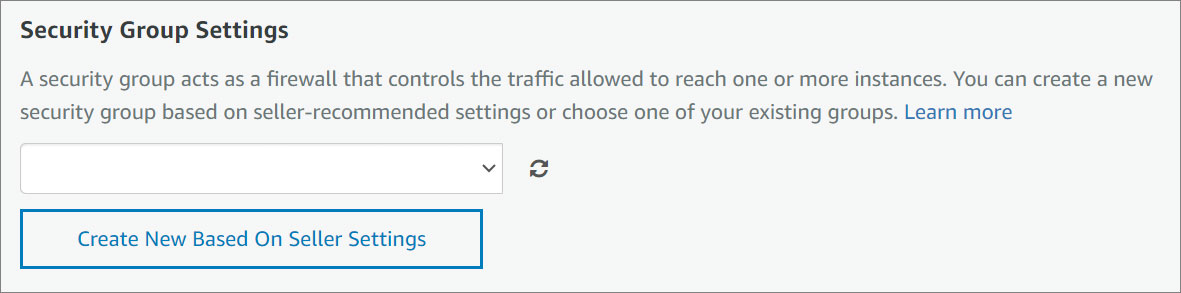
To learn more about security groups, click here .
- Key Pair Settings. An Amazon EC2 key pair is a set of security credentials consisting of a public and private key that verify a user’s identity when connecting or communicating with an EC2 instance. Select an existing security group from the menu or configure a new security group using the form provided.
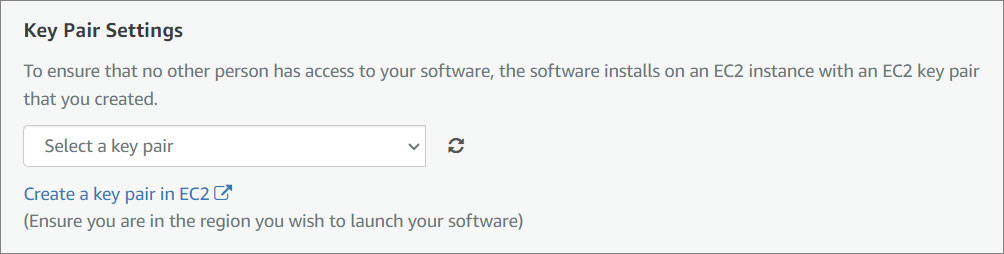
If you do not have a Key Pair, you will need to create one in your Key Pair Console. For instructions click here .
Click Launch.
You will receive a success message to view your instance. Click on EC2 Console.
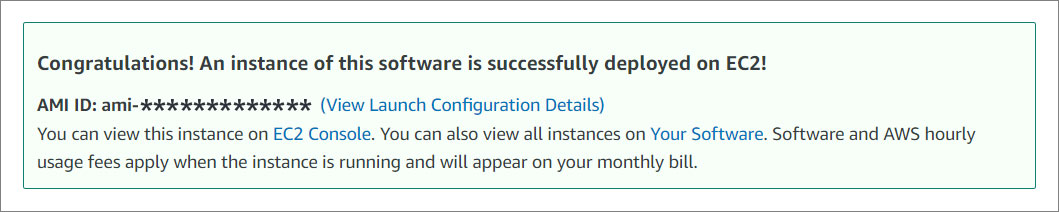
#
EC2 Instance
- Check the Instance State and Status Check of your instance. Once your instance state changed from Pending to Running, click on the instance you created to access it.

- To access the Drupal login page, add
/adminto the end of your Public IPv4 address.

Note:
Ensure that your browser's address bar includes "http://" instead of "https://."
- To log in, use drupal as the username and your instance ID as the password.
#
Next Steps

Drupal CDN
Prerequisites: you need a certificate with the name of site you are trying to launch
and have an existing Drupal.
Boost your site's speed by delivering content from servers near your visitors.
